Production Data Collection: The Ultimate Guide to PDC Systems [2025]
Our detailed guide to production data collection answers the following questions:
- What is production data collection?
- What kinds of production data are there?
- What are the benefits of capturing production data?
- What are the differences among production data collection, machine data collection (MDC), and manufacturing execution systems (MES)?
- How have production data collection systems worked in the past?
- What characterizes a modern production data collection system?
This article explains everything that you need to successfully implement a production data collection system. So let’s roll up our sleeves and get started!
What is production data collection?
Production data collection (PDC) is the systematic process of gathering, monitoring, and analyzing real-time manufacturing data from shop floor operations, including machine performance, work orders, quality metrics, and production cycles. This automated system enables manufacturers to track efficiency, optimize processes, and make data-driven decisions to improve productivity and reduce costs.
What kinds of production data are there?
Two kinds of production data can be distinguished: organizational and technical.
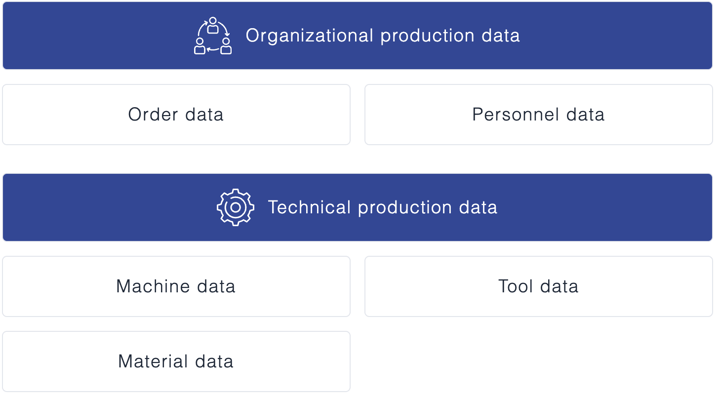
1. Order data
These are classic data such as ordered quantities and order processing times. They capture the status of production orders and the progress made in completing them, as well as order-related feedback.
2. Personnel data
Personnel data mainly comprise the times worked by personnel and possibly also the quantities they have produced, which can then be utilized to calculate wages or other staff-related metrics.

3. Machine data
Machine data include machine running times and stops, output and pieces produced, alarms, quality, and if required also energy consumption.
To ensure traceability (by documenting the manufacturing process), a large volume of very detailed quality data is also captured. These are usually clearly referenced to specific parts.

4. Tool data
Tool data are captured to monitor how tools are used in the manufacturing process, since in the final analysis they can crucially impact quality and the ability to produce.

5. Material data
Data on materials play an important role in connection with supplying, consuming, and stocking inputs and other logistical operations.
What are the benefits of capturing production data?
Depending on company-specific conditions and production-specific value creation processes, production data collection generates a variety of opportunities to make improvements. Some of the benefits are explained in the following:
Transparency in real time
Real-time monitoring of all process units makes it possible to immediately detect any downtimes or deviations from the plan, thus permitting early intervention and/or changing of plans if required.
Greater efficiency
Analyzing historical data and comparing desired and actual results can reveal weaknesses so that appropriate action can be taken to lastingly increase the efficiency of manufacturing processes.
Precise costing
Production data collection makes it possible to directly assign costs to the factors that incur them. The greater cost transparency achieved in this way improves monitoring and cost management.
Optimal planning of resources
Trustworthy, reliable, real-time data on all process units can support optimal utilization of machines with regard to their availability, performance and quality (overall equipment effectiveness).
Long-term competitiveness
Greater efficiency and quality improve the meeting of deadlines and greater customer satisfaction. This in turn maintains competitiveness and sustained growth.
Difference Between PDC, MDC, and MES Explained
Machine data collection (MDC)
This is a subset of production data collection. It only covers machine-related data that are generated during production, such as numbers of parts produced, energy consumption, and machine states.
Production data collection (PDC)
Production data collection systems collect not just machine data but also organizational data such as order and personnel data.
Manufacturing execution system (MES)
An MES is broader in scope than a typical production data collection system. It also includes, for example, functions for blocking process steps and ensuring traceability. The international ISA-95 standard covers MES functions in detail.

How have production data collection systems worked in the past?
Production data are generated where value is created, i.e. on the shopfloor where production personnel interact with various workplaces and/or production machines. Appropriate user-friendly (mobile) devices can be used in interplay with automated machine interfaces.
In the past, proprietary terminals were used to capture production data, which were then sent to a locally installed central database-based system. There the data were processed, evaluated, and exchanged with adjoining IT systems (for enterprise resource planning, production planning and control, advanced planning and scheduling, warehouse management etc.).
What characterizes a modern production data collection system?
In the age of digitalization, considerably more efficient methods and standardized technologies are now available. In the following, we will look at the most important benefits of a modern production data collection system:
 Simple installation
Simple installation
Production data collection functions can now be booked as software as a service (SaaS) via the cloud, thus eliminating capital-intensive investment and installation. This makes it easier for manufacturing companies to enter the digital world while minimizing the associated risks for decision-makers.
 High flexibility
High flexibility
Manufacturing companies constantly face changing requirements. Modern production data collection systems should therefore provide modular solutions that can be flexibly configured to meet production-specific requirements.
 Modern technology
Modern technology
These days, technologies change very rapidly. What is new today will be antiquated within just a few years. A modern production data collection system should be based on the very latest technologies and continually evolve to reap the benefits (such as greater performance and security) that technological change brings.
 Strong security
Strong security
IT security is imperative at companies. Very effective protection from external attacks and internal abuse is also indispensable for production data collection systems. They should therefore include powerful data encryption and maximum security for applications and the cloud.
 Connectivity
Connectivity
It’s common for companies to use multiple IT systems at the same time. To ensure problem-free communication among them, a production data collection system should be easy to connect to other systems. This can be accomplished, for example, by REST APIs or file-based interfaces.
How can I efficiently and cost-effectively implement a production data collection system?
For more information on this, please consult the sections on production metrics and production control, or have one of our experts show you in an one-on-one web session how quickly and easily this can now be done.




